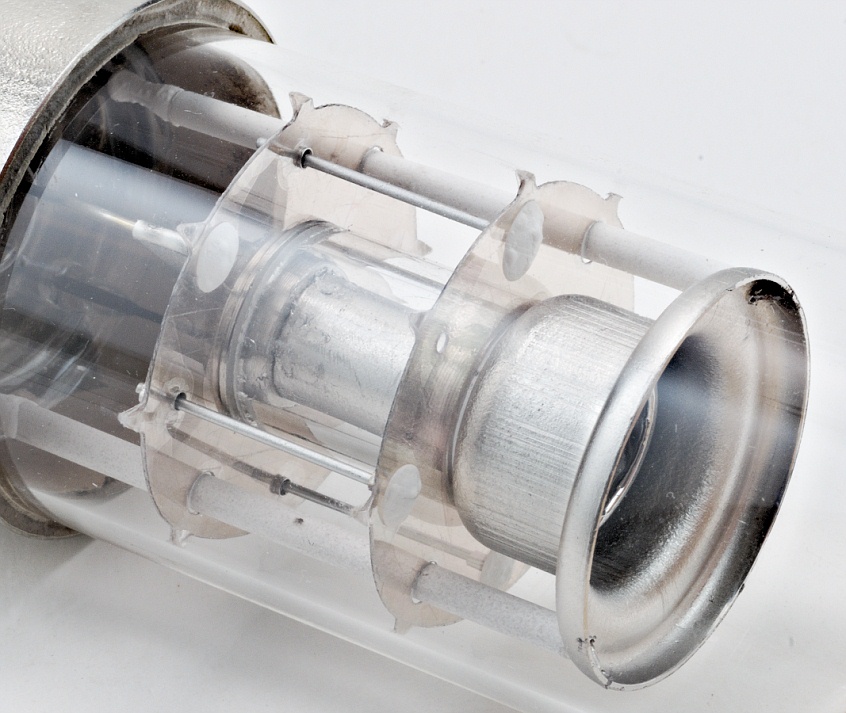


The release of this radiation allows for data to be collected and information gathered pertaining to the metal of interest. Some of these metal atoms in the cloud have moved to an excited energy state and as they return to their ground state, they emit a specific radiation which is characteristic to the metal of interest. The process of producing this cloud is called sputtering. The removal of these atoms produces a cloud around the cathode. If the voltage applied is large enough, the ions of the inert gas gather enough energy to remove some of the metal atoms of interest from the surface of the cathode by striking the surface. This current allows for electrons to move to the anode and cathode. This voltage is applied across the anode and the cathode and generates a current of 5-15 mA. Ionization is how neutral atoms are converted to charged species. First, the inert gas inside the glass tube is ionized by a voltage. The excitation process of the element of interest happens in a few steps. Excitation Process Hollow-cathode lamps in an atomic absorption spectrometer The material of the window is specifically selected in order to get the best transmission of spectral lines for the cathode element. Contamination of the cathode compromises the purity of the metal of interest and the data obtained for that metal. It is important that the cathode be stored under a vacuum to avoid any kind of contamination. The cathode is made of the pure metal of interest or a mixture of metals containing the metal of interest. The anode is typically constructed of an inert conducting metal to ionize the inert gas. The anode is an electrode in which loss of electrons by ionization takes place. It is important that the gas is inert in order to minimize interferences in the output of the data. The glass tube is filled with some type of inert gas such as argon or neon with a pressure of around 5 torr (666 Pascal). Instrument Design Diagram of a hollow-cathode lampĪ HCL consists of an anode and a cathode inside of a glass tube. These transitions can occur through heat, electrical energy, light, particles, or a chemical reaction. Excitation is when an electron in its lowest energy state, also known as the ground state, undergoes a transition to a higher energy state known as an excited state. The HCL is a light source or radiation source which is used to excite electrons of a metal of interest to a higher energy level. An HCL takes advantage of the hollow cathode effect, which causes conduction at a lower voltage and with more current than a cold cathode lamp that does not have a hollow cathode.
See the talk page for details.Ī hollow-cathode lamp (HCL) is type of cold cathode lamp used in physics and chemistry as a spectral line source (for example, in atomic absorption spectrometers) and as a frequency tuner for light sources such as lasers. Please help recruit one or improve this article yourself. An expert on the subject should have a look at this article or section.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
